Osteoarthritis of the knee joint is one of the most common diseases of the musculoskeletal system and, unfortunately, the most common cause of loss of mobility, disability and sometimes disability.With osteoarthritis, the cartilage that lines the joint surface is irreversibly affected, causing the correct functioning of the joint to stop and causing pain.
Officially the disease is called "deforming arthrosis";another name is gonarthrosis (from the ancient Greek “goni” - knee).The knee joints are the largest joints in the human body and are the ones most commonly affected by osteoarthritis.Much less commonly, the disease affects the hip and ankle joints.
How does gonarthrosis manifest itself?
Normally healthy cartilage is elastic and smooth, completely covering the mobile areas of the bone and allowing them to slide.Cartilage also reduces the stress that bones receive when walking or exercising.
When cartilage is destroyed (this is how arthrosis occurs), the upper layer of this elastic tissue becomes thinner.Sometimes the cartilage delaminates, tears appear - this is how the joint loses its main "shock absorber" and "bearing".The bones begin to rub against each other, the joint swells, gradually loses its normal appearance and pain appears.
Causes of gonarthrosis and risk factors
Deforming arthrosis is more common in older and overweight women, but this does not mean that young and physically active people do not suffer from this pathology.Sometimes the development of the disease is provoked by heavy physical work or excessive stress in the gym.
Here is a far from complete list of the causes of arthrosis of the knee joint:
- sports injuries - meniscal tears, fractures and dislocations;
- inflammatory processes in the joints and concomitant diseases;
- metabolic disorders: some diseases lead to the formation of intra-articular deposits;
- excessive stress on the joint, including prolonged standing or physical work associated with heavy lifting;
- uneven load on the joints due to the curvature of the legs: arthrosis occurs faster in overloaded areas.
Much depends on the genes: a person may have a hereditary predisposition to arthrosis of the knee joints.In these people, the gene responsible for the development and stability of cartilage tissue is disrupted.
There are several factors that increase the risk of gonarthrosis:
- increase in body weight.Due to the increasing load on the joint, the cartilaginous tissue wears out faster;
- aged over 40.Most people of this age have reduced physical activity.Due to physical inactivity, muscles atrophy, weak muscle tissue does not adequately nourish joints, and the risk of cartilage damage increases.
Symptoms of osteoarthritis
Osteoarthritis of the knee joint is not a disease that can appear suddenly.It makes itself known well in advance: it all starts with a slight pain in the knee when walking.The pain may increase if you have to go up or down stairs.As a rule, the knee hurts at the beginning of the movement, then the pain disappears and returns again with prolonged load on the joint.
If you ignore these symptoms and do not consult a doctor about it, the disease will begin to progress.Then the pain will change from temporary to continuous, the knee will start to hurt more even at rest, and will swell.As the cartilage deteriorates, the mobility of the entire joint will be limited.
Some people notice that their knee "reacts" to weather changes.This really happens: the nerve endings in the joint capsule are sensitive to changes in atmospheric pressure.
The following symptoms are characteristic of gonarthrosis:
- knee pain when moving and walking;
- morning stiffness of the knee joint, when the range of motion is minimal;
- knee swelling;
- dry and rough sound when moving: this sound occurs due to friction of the joint surfaces.
As the disease progresses, the symptoms will change:
- the pain will bother you even at rest;
- the joint becomes deformed and loses its functions;
- Due to the deformation of the knee, the gait will change.
Degrees of gonarthrosis
There are 3 stages of development of arthrosis of the knee joint.
1st degreedisease - almost asymptomatic.It begins with the first manifestations of the disease - almost painless, for example, fatigue in the legs - and lasts until the first bone deformities appear.If the knee has changed shape due to synovitis, that is, due to the accumulation of fluid in the joint, but the intra-articular cartilage is not damaged, the disease is still at stage 1.

2nd degreecharacterized by progressive changes in bone tissue.Externally, the knee may appear as in stage 1: deformed and enlarged.The pain increases: in addition to the incoming pain that occurs during movement, crepitus (crunching) in the affected knee is added.The joint becomes less mobile, it becomes difficult to squat and walk on uneven surfaces.
3rd degreethe degree of gonarthrosis is the most painful.At this stage there is almost no cartilage tissue left, and if the disease is severe, the bones may grow together.Subsequently the joint is completely immobilized and the person must move only with the help of a crutch or a cane.Usually at this point doctors give a verdict on the endoprosthesis of the damaged joint.
Important: only a doctor can determine the exact degree of development of the disease.Sometimes, with mild symptoms, the disease severely affects the cartilaginous membrane, therefore, for an accurate diagnosis, additional studies are usually carried out:
- x-ray - to see whether the cartilaginous surfaces are deformed and in what condition the joint space is located;
- CT or MRI - for more detailed studies.
How is gonarthrosis diagnosed and treated?
The first thing to remember is that timely diagnosis and early treatment will help stop the disease right from the start.Therefore, the appearance of the first discomfort in the knee joint is a good reason to visit a doctor and undergo an examination.
Doctors make a diagnosis of osteoarthritis based not only on the medical history, complaints and the current state of the knee joint.The results of further studies also play an important role: they are often prescribed to clarify the stage of gonarthrosis and the severity of the disease.
To accurately diagnose arthrosis of the knee joint, doctors usually prescribe:
- radiography.If pathological processes have begun in the knee - for example, deposits of calcium crystals or bone tumors have appeared in the joint capsule - these changes will be visible in the photographs.Doctors very often prescribe x-ray tests, but without a thorough examination of the knee joint, its mobility and the condition of the muscles that support it, the picture is incomplete;
- Ultrasound: Can be used to evaluate the condition of the soft tissues surrounding and lining the joint.Ultrasound complements the results of x-rays so that the doctor can see changes not only in bone structures, but also in tissues;
- MRI - magnetic resonance imaging.In case of knee pain, an MRI is prescribed if the doctor suspects damage to the meniscus, ligaments or tendons;
- Arthroscopy is an invasive examination in which the joint cavity is examined from the inside using a camera.The cameras are inserted through small incisions in the skin;through these same incisions, doctors can perform small manipulations, for example, remove a piece of destroyed cartilage, partially smooth out irregularities in the cartilaginous tissue, etc.
Treatment of arthrosis is usually carried out with drugs, first of all trying to relieve pain, improve joint mobility and restore the ability to move.Osteoarthritis causes irreversible changes in cartilage tissue, so it is impossible to talk about a complete cure.But it is possible to halt the progression of the disease and thus slow down further tissue destruction.
This is what the standard treatment for gonarthrosis looks like:
- local remedies: plasters, creams, ointments and gels;
- painkillers;
- anti-inflammatory drugs, especially non-steroidal.Their use is considered the “gold standard” of medicine, but these drugs destroy the gastric mucosa;
- blockades and chondroprotectors - drugs whose effect appears only after a long course of use;
- rarely - physiotherapeutic and sanatorium treatment.
It is recommended to wear orthopedic knee braces to support the joint and reduce pain.But all the methods listed above are methods of passive influence on the functioning of the joint.
This treatment relieves only some symptoms: neutralizes pain, inhibits inflammatory processes, etc.The disease itself continues to progress, gradually destroying the joint.In the final stages of osteoarthritis, a person loses not only the ability to work, but also the ability to move.In these cases it is necessary to prosthesis the joint, that is, insert an artificial structure into the knee.Such surgery does not pass without a trace and imposes its own limitations - and therefore reduces the quality of life.
Methods of active influence on the joint have a completely different effect, when, using the body's own resources, the tone of the muscles that supply the joint with blood and nutrients is restored.Such treatment is most effective if carried out under the supervision of qualified and experienced doctors.
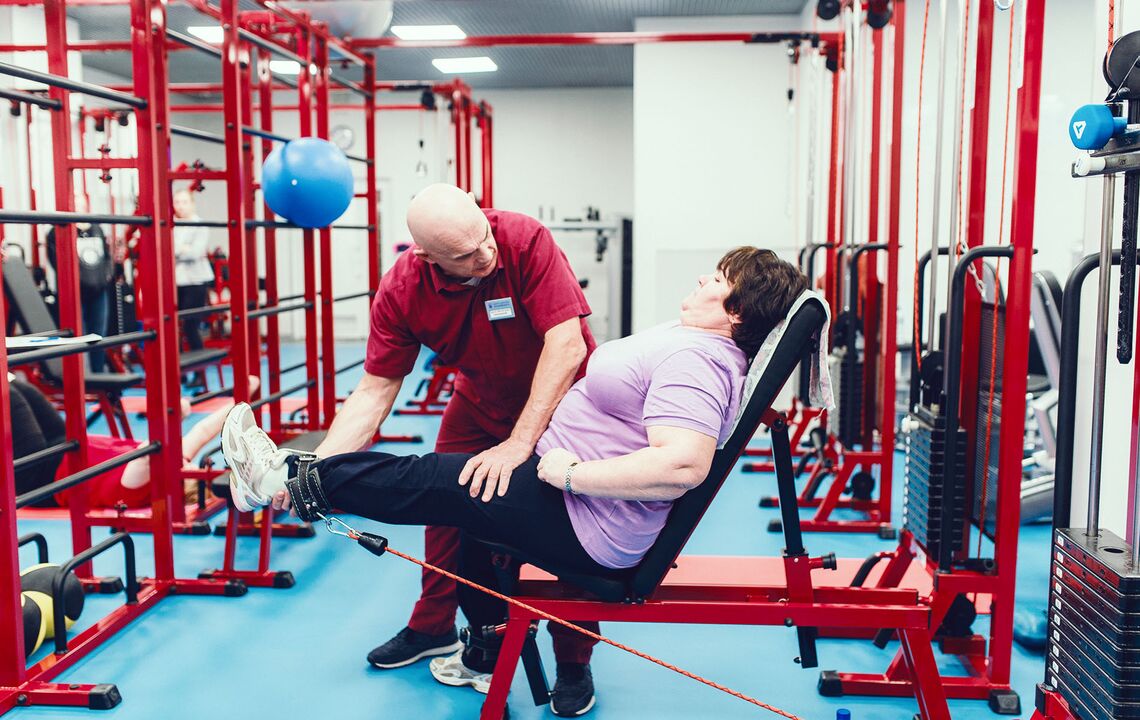
Treatment of gonarthrosis with kinesitherapy
Kinesitherapy, i.e. movement therapy, activates the body's own forces.Correctly selected load allows you to effectively work with the necessary muscles and, strengthening the muscle corset, improve the condition of the joints and cartilage.
Treatment with kinesitherapy begins with a thorough examination and, necessarily, a myofascial test.A kinesitherapist examines the condition of a painful knee, analyzes the condition of the muscle tissue, tendons and ligaments.Taking into account the data of ultrasound, CT, MRI and radiography, the degree of gonarthrosis is determined and a program of therapeutic exercises is drawn up.
Classes take place on a multifunctional simulator, a proprietary simulator with a special design.The exercises are performed in such a way as to avoid excessive stress on the joint and work only on those muscles that need to be strengthened and developed.In the initial stages, patients are prescribed joint gymnastics on the floor: it consists of exercises on a mat without weights.
The therapeutic effect of kinesitherapy is ensured by the restoration of blood microcirculation and the improvement of lymphatic drainage.The cartilage receives more nutrition, the development of arthrosis slows down to a complete stop, and the biomechanics of the joint joint are completely restored.
Such a serious disease as arthrosis of the knee joints cannot be ignored.The best way to prevent it is to lead a healthy lifestyle: balanced diet, physical activity.But if joint problems have already begun, you should not wait for serious warning signs: at the first symptoms you should seek help from qualified doctors.



























